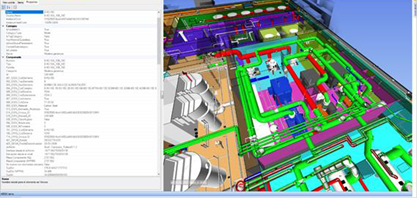
In User Story #2, the focus lies on evaluating the effectiveness of utilizing 3D/BIM models in the dismantling process, with a specific emphasis on comparing conventional methods with digitally enhanced techniques.
The primary data source for this user story, provided by ENRESA, was a comprehensive 3D/BIM model based on the Santa Maria de Garona (SMG) facility.

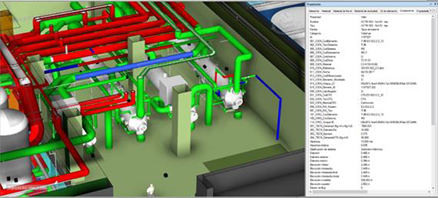
The input data for this model encompassed crucial details, such as a BIM model of the component, the surrounding area, and the path to be followed in the User Story. Additionally, the dataset comprised design drawings and specifications for the component earmarked for removal, radiological characterization of the area housing the component, as well as the transportation path to be followed. Physical parameters of the component, such as mass, material thickness, density, and other pertinent details, were integral components of the input. Furthermore, the dataset incorporated a comprehensive plan detailing the activities slated for completion.
To verify and complete the database, the incorporation of point clouds was proposed. As no existing point cloud was available in the beginning, two solutions were implemented: creating a point cloud through photogrammetry by KIT and performing a scan campaign by Quadrica.
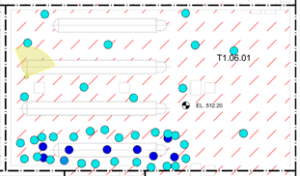

Point cloud view from 3DScanPF, and superimposition with the 3D model of the heater (3DScanPF, KIT)
The anticipated outcomes encompassed a comparison between conventional and digitally enhanced support provided by PLEIADES. The evaluation aimed to monitor PLEIADES’ efficiency across various parameters such as dose rate, scheduling, costing, waste production, safety, and risk management. The objectives included the practical implementation of tasks outlined in the test procedure, contrasting the basic use of 3D models with the advanced capabilities of the digitally enhanced dismantling toolkit. Additionally, the expectations involved acquiring dose maps and radiological 3D models (activity/contamination maps) directly from the tools integrated into PLEIADES. The anticipated advancements also encompassed further development utilizing XR visualization and execution, enabling users to navigate and experience work tasks in real-size environments.
The testing procedure was carried as follows, unfolding with sequential steps:
- Load 3D model (optionally point cloud) of the component and the area;
- Identify and update whether the component (or the system the component is part of), is relevant for safety or not;
- Model the dose distribution, based on measurements from radiological characterization of:
– The component and the system it is part of;
– The disassembly area;
– The transportation route. - Enable animation of the element in the 3D model (move, rotate) and define sequence of activities (work order) with specific information for all involved disciplines;
- Estimate dose exposure of workers;
- Simulate and visualize the sequence of activities in the 3D model and execute them in XR;
- Estimate time schedule, costs for work orders, and waste quantities;
- Perform sensitivity analysis on selected input parameters, save data and test results;
- Assess the radiological risks in terms of ALARA and worker safety;
- Compare the alternative dismantling scenarios.
Results were obtained with the use of different tools:
- Verification of the accuracy and increase of the models LOD were carried out thanks to the point cloud data obtained with 3DScanPF and the scan campaign of Quadrica;
- Simulation of the evacuation path was assessed with DEMPlus®;
- Results regarding costs allocations, collective dose, and waste quantities were obtained with DEMPlus®;
- Workers dose estimation was carried out with iDrop;
- Estimation of costs, amount of generated waste, and waste stream simulation was obtained with Aquila Costing;
- The sequence of activities was visualized and executed using XR Workflow application.
Follow the project’s LinkedIn page and subscribe to our newsletter to keep up-to-date with the project’s progress!
